Top 10 brake mistakes technicians can make.
1. Neglecting brake slides and hardware: Merely placing new pads and abutment clips where the old ones were won't suffice. The caliper bracket slides must be clean and rust-free. Avoid excessive force with a wire brush, especially since some automakers apply anti-corrosion coatings to brake caliper bracket lands. If deposits persist after using brake cleaner and a nylon brush, using a wire wheel or file may worsen corrosion.
2. Neglecting guide pin lubrication: Many shortcut methods overlook this step. Guide pins on floating calipers should be thoroughly cleaned with solvent, and fresh grease should be applied. Since the grease is subjected to high heat and pressure, it's crucial to use grease specifically designed for calipers. Never reinstall a torn boot on a car. Failure to maintain the guide pins is a primary cause of uneven pad wear. Additionally, avoid using impact tools to remove or install guide pins, as most guide pins are plated with anti-corrosion material, and spinning them in a bore could damage the plating.
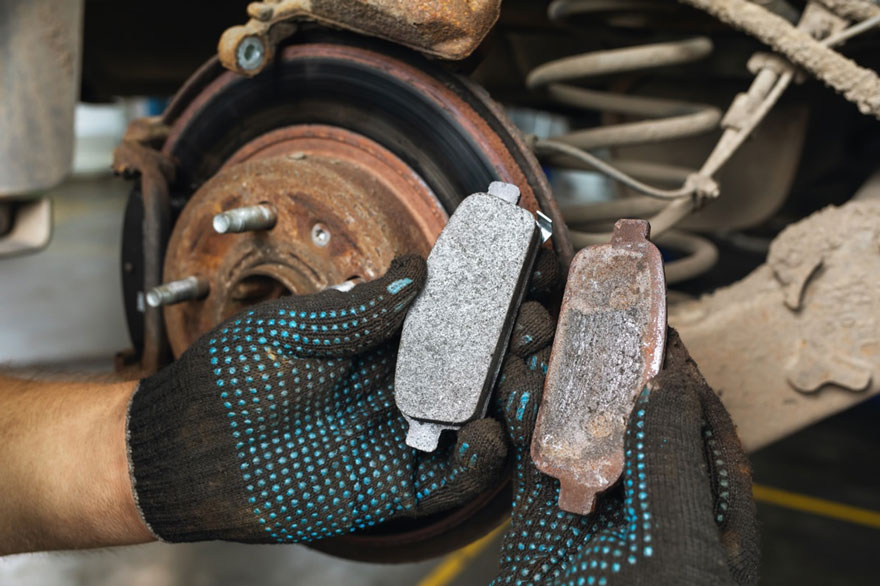
3. Reversing Brake Pad Installation: A Common Occurrence! When a vehicle enters your workshop, the owner often complains about friction noise in the braking system after replacing the car brake pads.
4. Neglecting Disc Measurement: It is crucial to measure the thickness and runout of the brake discs consistently. Using discs that do not meet specifications can result in safety issues, such as cracks and diminished braking performance. Furthermore, failure to address lateral runout may lead to complaints of shimmying during braking.
5. Neglecting to machine the rotor when installing new pads is a common oversight. A fresh rotor surface is essential for optimal brake performance, enabling new pads to deposit a thin layer of friction material. Old deposits on the rotor can contaminate the new pads, leading to performance and noise issues.
6. Not properly torquing the caliper bracket bolts: Not all caliper bracket bolts are the same. Torque ranges can vary from 30 to 110 ft./lbs. Also, some bracket bolts can be torque-to-yield or require liquid tread lockers. If you see an aluminum knuckle, look up the torque specifications.
7. Over-torquing caliper guide pin bolts is a common rookie mistake. Using excessive force can lead to bolt breakage, but usually, only 25 to 35 ft./lbs. of torque is needed, so apply gentle pressure with a 13 mm wrench.
8. Installing a caliper upside down is a major issue during bleeding. If bleeders are at the bottom instead of the top, it's challenging to remove all the air. Always confirm left and right calipers before starting the job to avoid this mistake.
9. Choosing inexpensive brake pads solely based on price, without considering quality, features, and reputation, is a common mistake, especially for beginners.
10. Hanging a brake caliper by the hose is a damaging mistake. It can harm the hose's internal structure, leading to issues like a soft pedal or even a rupture. Avoid this to ensure proper brake system function.
What is friction material?

Friction materials are components applied to power machinery, relying on friction to perform braking and transmission functions. They mainly include brake linings and clutch facings. Brake linings are used for braking, while clutch facings are used for transmission.
Any mechanical equipment and various vehicles in motion must have braking or transmission devices. Friction materials are crucial components in these braking or transmission devices. Their primary function is to absorb or transmit power through friction. For example, clutch facings transmit power, and brake linings absorb kinetic energy. They enable mechanical equipment and various vehicles to operate safely and reliably. Therefore, friction materials are widely applied and play a crucial role in various applications.
Types of Asbestos-Free Friction Materials.
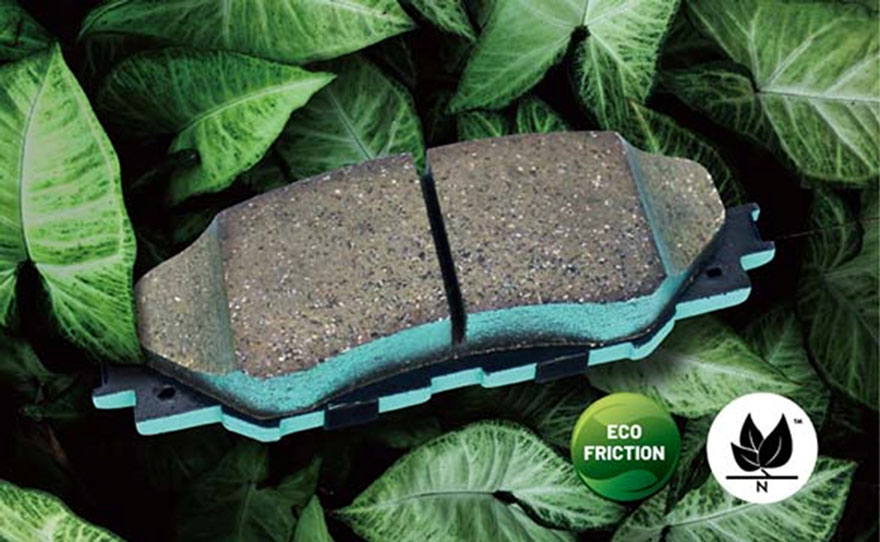

1. Semi-metallic Friction Materials: Applied to disc brake pads for sedans and heavy-duty vehicles. The composition typically includes around 30% to 50% of ferrous metallic substances (such as steel fibers, reduced iron powder, foam iron powder). It is named semi-metallic due to the presence of these iron-based metallic components. It is one of the earliest materials developed as an asbestos-free alternative. Features: Good heat resistance, high power absorption per unit area, high thermal conductivity, suitable for braking under high-speed and heavy-load conditions in automotive applications. However, it has drawbacks such as significant brake noise and edge cracking.
2. NAO Friction Materials: Broadly refers to non-asbestos, non-steel fiber friction materials, although a small amount of steel fibers is present in modern disc brake pads. The base material in NAO friction materials is typically a mixture of two or more fibers (mostly inorganic fibers, with a small amount of organic fibers). Therefore, NAO friction materials are non-asbestos mixed fiber friction materials. Brake linings are usually short fiber types, while clutch facings are continuous fiber types.
3. Powder Metallurgy Friction Materials: Also known as sintered friction materials, these are produced by mixing and pressing powdered materials, typically iron-based or copper-based, and sintering them at high temperatures. Suitable for braking and transmission under higher temperature conditions, such as in aircraft, heavy-duty trucks, and heavy construction machinery. Pros: Long service life; Cons: High product cost, significant brake noise, heavy and brittle, substantial wear on mating surfaces.
4. Carbon Fiber Friction Materials: A type of friction material made using carbon fibers as reinforcement. Carbon fibers have high modulus, good thermal conductivity, and heat resistance. Carbon fiber friction materials exhibit the best performance among various types of friction materials. The unit power absorption per area of carbon fiber friction pads is high, and they are lightweight, making them particularly suitable for producing aircraft brake linings. Some high-end cars abroad also use carbon fiber brake pads. Due to their high cost, their application is limited, and production is relatively low. In the composition of carbon fiber friction materials, besides carbon fibers, graphite and carbon compounds are also used. The organic binding agents in the composition also undergo carbonization treatment, so carbon fiber friction materials are also referred to as carbon-carbon friction materials or carbon-based friction materials.
For heavy motorcycles with engine displacements exceeding 250cc, what is recommended?Why is this material recommended?

For heavy motorcycles with engine displacements exceeding 250cc, it is recommended to use semi-metallic brake pads or ceramic compounds material brake pads. These materials typically offer better heat resistance, durability, and braking power to ensure safety and performance during high-speed riding and sudden braking. Or use the “Contact us” form, an agent will be assigned to assist you.ADUI-Motorcycle brake pad brand recommendations!
MOTORCYCLE | Click here
When replacing the brake pads on a motorcycle with new ones, if the tire cannot be turned, is this normal?

Of course, this is not normal. After replacing the motorcycle brake pads with new ones, if the tire does not turn when rotated by hand or turns with great difficulty, it indicates that the brake pads are gripping the disc. In this case, clean the caliper pistons, push them back to the bottom, and reinstall the brake pads to resolve the issue!
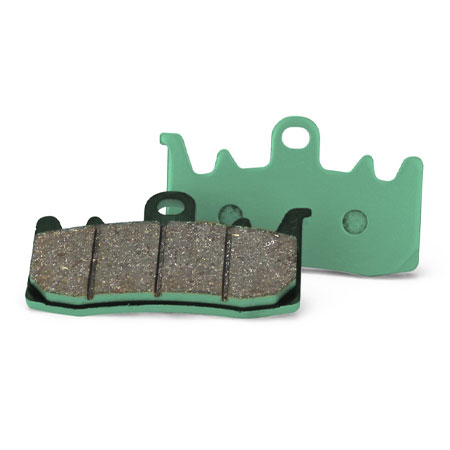
What materials of motorcycle brake pads do you offer, and what are the characteristics of different materials?Can I customize brake pads?"

We offer three versions of motorcycle brake pads and also provide customized brake pad services. ADUI BRAKE INDUSTRY INC. - brake pads company.One of the best OEM & ODM disc brake pads manufacturer in Taiwan.Feel free to Contact Us anytime."
Street Aggressive Version
Characteristic
Organic Compounds/Ceramic
Low dust
Low noise
Temperature: 0-400°C
Advantage
Low abrasion
Long-lasting
Environmental protection
Rotor friendly
Application
Suitable for riding frequently.
For commuter and leisure use.

Sports Version
Characteristic
Ceramic Compounds
Low dust
Low noise
Temperature: 0-500°C
Advantage
Middle abrasion
Braking performance and temperature resistant are better than genuine parts.
Environmental protection
Rotor friendly
Application
For mountain road, commuter, and sometime heavy riding users.
Suitable: down to 250cc motorcycle / scooter

Heavy-Racing Version
Characteristic
Ceramic Compounds
Middle dust
Slight noise
Temperature: 0-600°C
Advantage
High temperature resistant suitable for heavy-racing
Excellent braking power with high friction
Application
For the demands of competition, downhill and high performance use.
Up to 250 cc type Suitable